Left Leaning Red Black Tree

A left leaning Red Black Tree or LLRB is a variant of red black tree which is a lot easier to implement than Red black tree itself and guarantees all the.
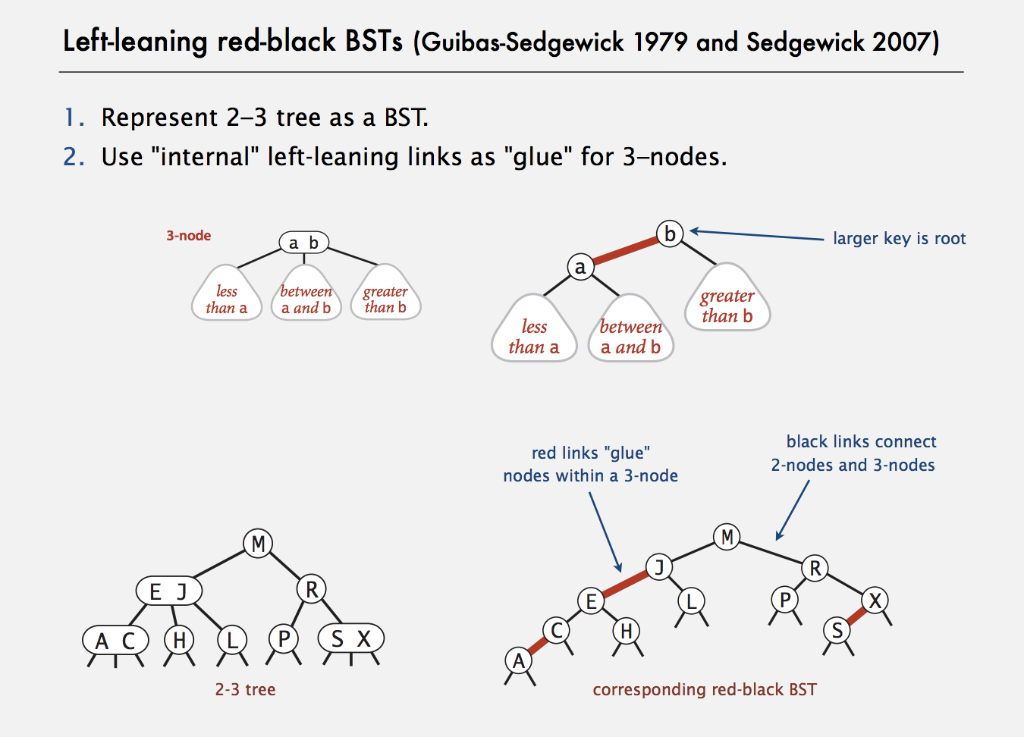
Left leaning red black tree. Robert Sedgewicks left-leaning red-black trees are supposedly simpler to implement than normal red-black trees. Insert 1 then 2 as a red edge then fix up the 1-2 tree then add 3 fix up the tree. Node RPutNode p const K.
It also provides a keys. In 2008 Sedgewick introduced a simpler version of the redblack tree called the left-leaning redblack tree by eliminating a previously unspecified degree of freedom in the implementation. They can be implemented by adding just a few lines of code to standard BST algorithms.
- ordered methods for finding the minimum maximum floor and ceiling. In addition to the usual rules of a red-black tree an LLRB adds the following rules. A left leaning Red Black Tree or LLRB is a variant of red black tree which is a lot easier to implement than Red black tree itself and guarantees all the search delete and insert operations in Ologn time.
Experimental studies have not been able to distinguish these algorithms from optimal. Use internal red edges for 3-nodes and 4-nodes. Description of 234-trees using Sedgewicks slides.
Nodes which have double incoming edge are RED in color. The original left-leaning red-black trees allows nodes whose two children are red that is this algorithm is another representaion of 2-3-4 trees. Draw the LLRB that results from inserting these items in the given order.
Im learning Red Black Trees RBT through Sedgewicks Algorithms - 4th Edition. Because the tree is arranged with all 3-nodes leaning to the left there are fewer special cases to handle in the code. Now his Red-black tree code is easy to remember.